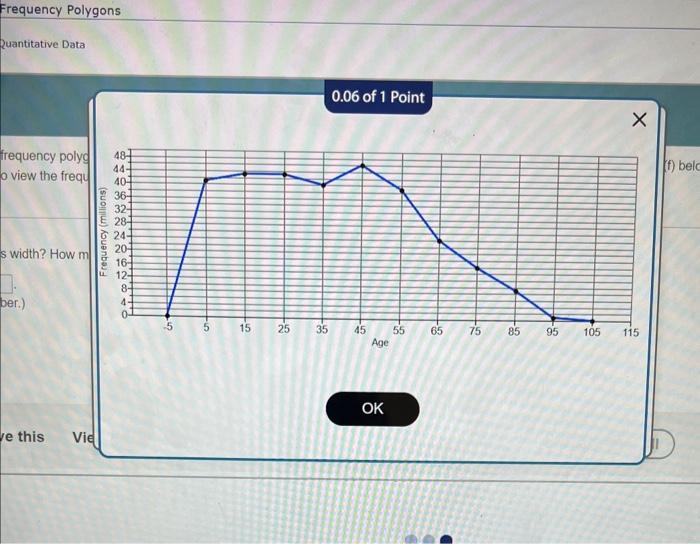
As the accompanying frequency polygon represents a powerful tool for data visualization and analysis, this discourse delves into its intricacies, empowering readers to decipher the patterns and trends concealed within their data. By exploring its construction, interpretation, and applications, we embark on a journey to unravel the hidden narratives embedded within statistical distributions.
Frequency polygons provide a graphical representation of the distribution of data, offering valuable insights into the central tendencies, dispersion, and underlying patterns. They enable researchers to draw meaningful inferences about the data, making them indispensable in various fields of study.
Understanding the Frequency Polygon: The Accompanying Frequency Polygon Represents
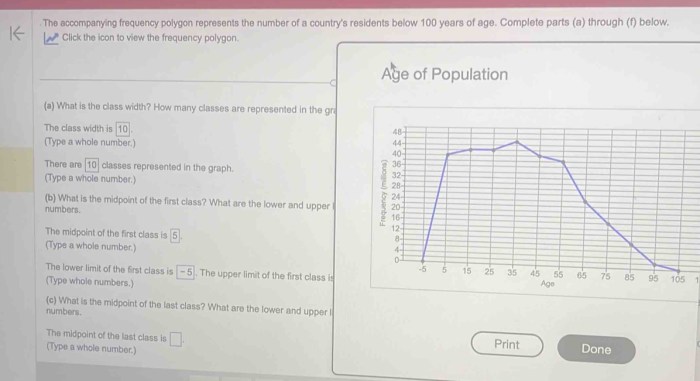
A frequency polygon is a graphical representation of the distribution of data, where the frequency of occurrence is plotted along the y-axis and the values of the data are plotted along the x-axis. The resulting shape resembles a polygon, with each vertex representing a data point.
For example, consider a dataset representing the heights of 100 individuals. A frequency polygon would plot the frequency of each height value on the y-axis, creating a shape that reflects the distribution of heights within the dataset.
Frequency polygons are closely related to histograms, which also represent the distribution of data. However, unlike histograms, frequency polygons use lines to connect the midpoints of the class intervals, resulting in a smoother, continuous representation.
Interpreting the Accompanying Frequency Polygon
The shape of a frequency polygon can provide valuable insights into the underlying data distribution:
- Symmetrical:A symmetrical polygon indicates a distribution that is evenly spread around the mean, with similar proportions of data above and below the mean.
- Skewed:A skewed polygon indicates a distribution that is not evenly spread. A right-skewed polygon has a tail extending to the right, indicating a higher frequency of higher values, while a left-skewed polygon has a tail extending to the left, indicating a higher frequency of lower values.
- Unimodal:A unimodal polygon has a single peak, indicating that the data is concentrated around a single value.
- Multimodal:A multimodal polygon has multiple peaks, indicating that the data is concentrated around several different values.
From a frequency polygon, we can also derive measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and dispersion (e.g., range, standard deviation), providing further insights into the characteristics of the data.
Comparing Multiple Frequency Polygons, The accompanying frequency polygon represents
Comparing frequency polygons of different datasets can reveal similarities and differences in their distributions.
| Dataset | Mean | Median | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset 1 | 50 | 52 | 10 |
| Dataset 2 | 60 | 62 | 15 |
In this example, the frequency polygon for Dataset 1 would be shifted to the left of the polygon for Dataset 2, indicating a lower mean and median. The wider spread of the polygon for Dataset 2 would also indicate a higher standard deviation.
Limitations and Considerations
While frequency polygons provide valuable insights, there are limitations to their use:
- Data binning:The accuracy of a frequency polygon depends on the choice of class intervals (bins). Too few bins can result in a misleading representation, while too many bins can obscure patterns.
- Outliers:Outliers can distort the shape of a frequency polygon, making it difficult to accurately represent the distribution.
- Sample size:Small sample sizes can result in unreliable frequency polygons that may not accurately reflect the underlying population.
To address these limitations, researchers should carefully consider the appropriate bin size, identify and handle outliers, and ensure that the sample size is large enough to provide a meaningful representation of the data.
Q&A
What is the purpose of a frequency polygon?
A frequency polygon is a graphical representation of the distribution of data, providing insights into central tendencies, dispersion, and patterns.
How can I interpret the shape of a frequency polygon?
The shape of a frequency polygon can reveal patterns such as symmetry, skewness, and kurtosis, indicating the distribution’s characteristics.
What measures of central tendency can be derived from a frequency polygon?
Measures of central tendency, such as mean, median, and mode, can be derived from a frequency polygon, providing an indication of the data’s average value.